Text Size :
Skin Disorders caused by Cosmetics
We use cosmetics to make ourselves look better, but sometimes a make-up allergy can cause some unsightly skin conditions instead.
- Article last reviewed 09 May 2019
- 8 mins read
Read section:
Irritant Cosmetic Dermatitis
This is the most common skin disorder that can be caused by cosmetics. The most frequent complaint is a rash and facial itching.
Types of cosmetics that may cause irritant contact dermatitis include:
• Facial cleansers: these often contain surfactants that are necessary to clean the skin
• Toners and astringents: these may contain alcohol or acids such as alpha-hydroxyacid (AHA), which can cause skin problems in some people
• Facial treatment: this involves the use of manual manipulation and application of chemicals on the skin, often resulting in exfoliation of the upper skin surface. Mild irritation is inevitable, but severe skin inflammation like dermatitis can occur
Excessive or inappropriate use of any of these skin care products and procedures can cause skin irritation, especially in individuals with sensitive skin or underlying skin diseases.
Signs and Symptoms of Irritant Cosmetic Dermatitis
The patient may experience only a burning or stinging sensation after applying the cosmetic on the skin, but in severe cases, itchiness, redness, swelling and later scaling and peeling of the skin can occur.
Treatment of Irritant Cosmetic Dermatitis
Stop using all cosmetic products on the affected skin immediately and consult your doctor. Do not seek treatment from beauticians or other medically unqualified people. Your doctor will treat you with a bland facial cleanser and low-potency corticosteroid cream or ointment.
After the rash has cleared, patch testing may be required at a later date to exclude an allergy to the cosmetics. Your doctor will advise you on the appropriate cosmetics to use.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Another important skin disorder caused by cosmetics is allergic contact dermatitis, which occurs less frequently than irritant contact dermatitis. It is often difficult to differentiate between the two by the appearance of the rash alone. Cosmetics ingredients that can cause skin allergy include fragrances, preservatives and sunscreens.
Symptoms and Signs of Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The patient may not experience any problem with the cosmetic initially. An allergic reaction can occur even after repeated exposure to the substance.
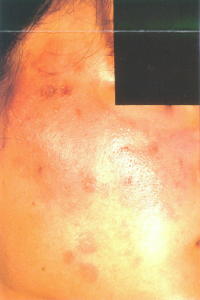
Symptoms include itchiness, redness, swelling or even blistering on the affected skin. Secondary spread beyond the affected site may occur. The same reaction will recur if the patient uses another product that contains the same ingredients.
Treatment for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
You should stop applying all cosmetics on the affected skin or anywhere else immediately. Your doctor will prescribe a topical or — in severe cases — oral corticosteroid to reduce the skin inflammation. Oral antihistamines may reduce intense itching. Patch testing should be done when the rash subsides to ascertain the cause of allergy.
Patch testing is a procedure that helps your dermatologist to identity the exact substance that you are allergic to. During the test, pieces of tape will be plastered on the back for 48 hours. You will return after 72 hours and/or a week later to determine if there is any allergic reaction. You will be tested with specially prepared patch test material and also with your own cosmetic products. After the evaluation, you can then be given appropriate advice as to which substance/s you must avoid in future.
Cosmetic-induced Pimples (Acne)
Acne or pimples can occur in patients who may or may not have a past history of adolescent pimples. Some cosmetics, e.g. foundation and moisturisers which are left on the skin for a long period of time, can cause comedones (“blackheads” or “whiteheads”) and inflamed pimples to appear.
Patients with cosmetic-induced pimples are treated as for ordinary pimples, i.e. appropriate creams/gels with or without oral medication, depending on the severity. Patients should preferably stop using all cosmetics until the skin improves. However, if the patient is uncomfortable with blemishes on the skin during the healing process, they should use oil-free or low oil-content cosmetics.
Special Cosmetic Allergies
Hair-dye allergy is one of the most common causes of cosmetic dermatitis in men and women. Some people are able to dye their hair initially without any problem, but may suddenly develop an allergy to the dye after repeated use. The face, ears and neck are often affected.
The substance in hair dye that often causes an allergy is para-phenylenediamine (PPD). It can be found in almost all brands of permanent hair dyes. Those who are allergic to PPD hair dyes must avoid all synthetic chemical hair dyes. The only suitable substitutes are henna, a vegetable dye, or metal pigment dyes.
Sunscreens protect our skin from sun damage. However they can also cause skin problems. Besides being sold commercially as sun-blocking agents, they are also incorporated into numerous cosmetic products such as lipsticks and facial foundation.
Sunscreens can cause irritant contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis and photoallergic contact dermatitis. Photoallergic dermatitis differs from allergic contact dermatitis, as the rash occurs only after the skin comes into direct exposure with the combination of the allergic substance and sunlight.
All chemical sunscreens have the potential to cause photoallergic dermatitis. Physical sunscreens, which contain metal elements, such as titanium dioxide, do not cause this problem.
Consult a dermatologist for a skin patch test if you suspect that you have sunscreen allergy. After the patch test, your dermatologist should be able to advise you on the type of sunscreen that you can use.
Read these next:
Contributed By
- National Skin Centre
Related support and tools
Related Topics
Explore some of these related topics
